Introduction
The world of frontend development is dynamic, with tools and frameworks constantly evolving. Among the frontrunners, React and Next.js stand out, each offering unique capabilities. As we dive into their intricacies, we’ll explore the latest updates and how they compare in the current development landscape.
A Closer Look at React
Originating from Facebook’s labs, React has transformed UI development. Its declarative nature, combined with JSX, facilitates the creation of interactive user interfaces. React’s component-centric architecture ensures that even complex UIs can be broken down into manageable, reusable pieces. Here I would like to inform you that React is just a library for UI development.
Kickstarting with React
As per the official documentation by React, it recommended picking one of the React-powered frameworks popular in the community such as NextJS or Remix. But if anyone wants to try or use only React, they can use Vite or CRA(create-react-app) tools.

Strengths of React
Intuitive Design with JSX
Explanation: JSX (JavaScript XML) is a syntax extension for JavaScript. It allows developers to write UI components using a syntax that looks very much like HTML. This blending of JavaScript and HTML means developers can easily create interactive UIs in a more readable and intuitive way.
Benefits: This reduces the cognitive load on developers and makes the codebase easier to understand and maintain.
Component Reusability
Explanation: One of the core principles of React is the creation of reusable UI components. Once a component is developed, it can be used across multiple parts of an application or even across different projects.
Benefits: This approach leads to consistent UIs, less repetitive code, faster development times, and easier maintenance.
Performance with Virtual DOM
Explanation: The Virtual DOM is a lightweight copy of the actual DOM in the browser. When changes are made, they’re first performed on the Virtual DOM. Only the differences (or “diffs”) between the previous and new state are updated in the real DOM.
Benefits: This minimises direct DOM manipulations, which can be slow, leading to smoother and faster UI updates.
SEO Capabilities
Explanation: While single-page applications (SPAs) built with JavaScript frameworks can face SEO challenges, React can be optimised for search engines using third-party tools like Next.js or by utilising React Server Components.
Benefits: This means React apps can achieve good search engine rankings, ensuring better visibility and reach for web-based projects.
Community Support
Explanation: React, being developed and maintained by Facebook, has gained immense popularity. As a result, there’s a vast community of developers, tons of educational resources, plugins, and tools available.
Benefits: This community support makes it easier for developers to find solutions to problems, learn best practices, and leverage open-source tools to enhance their applications.
Shortcomings of React
Fast-paced Updates
Explanation: React’s library receives frequent updates. While this means continuous improvement, it can sometimes be overwhelming for developers to keep up with the changes.
Impact: Teams may need to invest time in updating their applications to ensure compatibility, which can affect project timelines.
Documentation Gaps
Explanation: Due to the rapid evolution of React, the official documentation might not always reflect the latest practices or address all emerging challenges. This can leave developers reliant on community-driven content, which can vary in quality.
Impact: Newcomers or even experienced developers might face difficulties in finding the most accurate or up-to-date information on certain topics.
External Dependencies
Explanation: React is often described as the ‘V’ in the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture, focusing mainly on the view layer. As a result, for certain functionalities like routing or state management, developers might need to rely on third-party libraries.
Impact: This can introduce additional complexities into the development process, such as learning curves associated with these tools or potential compatibility issues.
Exploring Next.js
Next.js, a brainchild of Vercel, is more than just a frontend framework as it enables developers to write APIs within the project along with React Components. It comes packed with features like server-side rendering, static site generation, and more, making it a top choice for developers prioritising performance and SEO.
The Power of Next.js
Unlike React, which requires external libraries for functionalities like routing, Next.js has these built-in. This integrated approach simplifies development, eliminating the need for multiple dependencies.
Client-Side Rendering vs. Server-Side Rendering
While React primarily uses Client-Side Rendering (CSR), Next.js introduces the concept of Server-Side Rendering (SSR). In CSR, the application’s user interface is dynamically generated by the browser using JavaScript. This means when you inspect a React app’s source code, you’ll often see minimal content, with most of the UI being rendered dynamically on the client side.
On the other hand, Next.js employs SSR, where the user interface is generated on the server. This means the content is already prepared and sent to the browser, making the initial page load faster. When inspecting the source code of a Next.js app, you’ll see the entire content, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Strengths of Next.js
Efficiency with Integrated Features
Explanation: Next.js provides a range of out-of-the-box features such as routing, API routes, and image optimization. These built-in features save developers from manually setting up these functionalities.
Benefits: It streamlines the development process, reduces coding effort, and minimises the risk of errors.
Performance Enhancements
Explanation: Next.js offers built-in support for Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG). This ensures that web pages are pre-rendered, leading to faster page loads.
Benefits: Improved user experience due to faster loading times and a more responsive interface.
Enhanced SEO
Explanation: Thanks to its pre-rendering capabilities, Next.js ensures that the content of a page is available to search engine crawlers, even if it’s a Single Page Application (SPA).
Benefits: Web pages built with Next.js are more likely to rank higher on search engines, leading to increased visibility and organic traffic.
Configurability through Plugins
Explanation: Next.js provides a plugin system that allows developers to add tailored functionalities to their applications without rewriting large portions of the core codebase.
Benefits: This system ensures that applications remain scalable and can be enhanced or updated according to specific needs with minimal disruption.
Shortcomings of Next.js
File-system-based Routing
Explanation: Next.js uses a file-system-based routing mechanism. The structure of your pages directory dictates the routes of your application.
Impact: While this approach is intuitive, it might be too rigid for some applications that require more dynamic or complex routing setups.
Community Size
Explanation: While Next.js is gaining traction, its community is still growing and doesn’t yet match the vast, established base that React boasts.
Impact: This means there might be fewer resources, plugins, and third-party solutions available compared to more established frameworks.
Fast-paced Updates
Explanation: Similar to React, Next.js undergoes frequent updates. This constant evolution can sometimes make it difficult for developers to keep up.
Impact: Regular updates might necessitate changes to existing projects, adding to maintenance efforts and potential downtimes.
Learning Curve
Explanation: Next.js introduces its own conventions, especially around routing. For those used to client-side routing with libraries like React Router, this can require some adjustment.
Impact: Developers might need additional time and resources to familiarise themselves with the Next.js way of doing things, potentially slowing down initial development phases.
React vs. Next.js: A Comparative Analysis
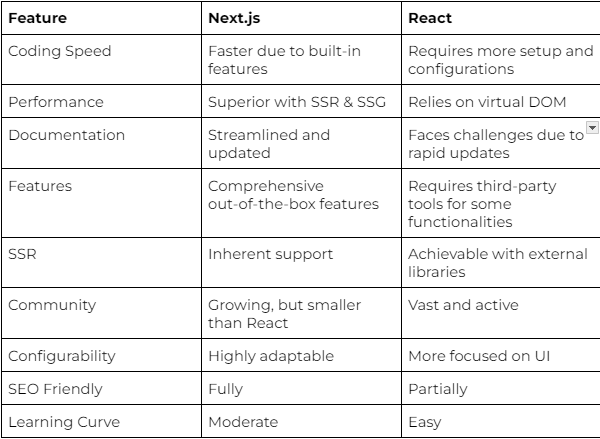
Ideal Use Cases
React: Perfect for dynamic websites, mobile apps, and platforms like Facebook, Netflix, and Airbnb especially Single Page Applications.
Next.js: The go-to for landing pages, e-commerce platforms, and high-performance sites, with examples like Twitch.tv and TikTok such as Multi-Page Applications.
Conclusion
Always keep this in mind that React is a library and NextJs is a framework which uses React for UI development. Choosing between React and Next.js boils down to the project’s specific needs. React’s flexibility is unmatched for dynamic UIs, while Next.js offers performance enhancements with server-side rendering. With the recent updates, such as Next.js 13.5 and React 18, both tools continue to evolve, offering developers a plethora of choices.
FAQs
Why use Next.js over React?
Is Next.js better than React?
Is Next.js faster than React?
Do I need Next.js for React?
What are the limitations of Next.js and React?

Written By- Lucas Samuel
PROJECT MANAGER
Digital Strategist | SEO Analyst | Website Analytics Expert
10+years experience in digital marketing Industry